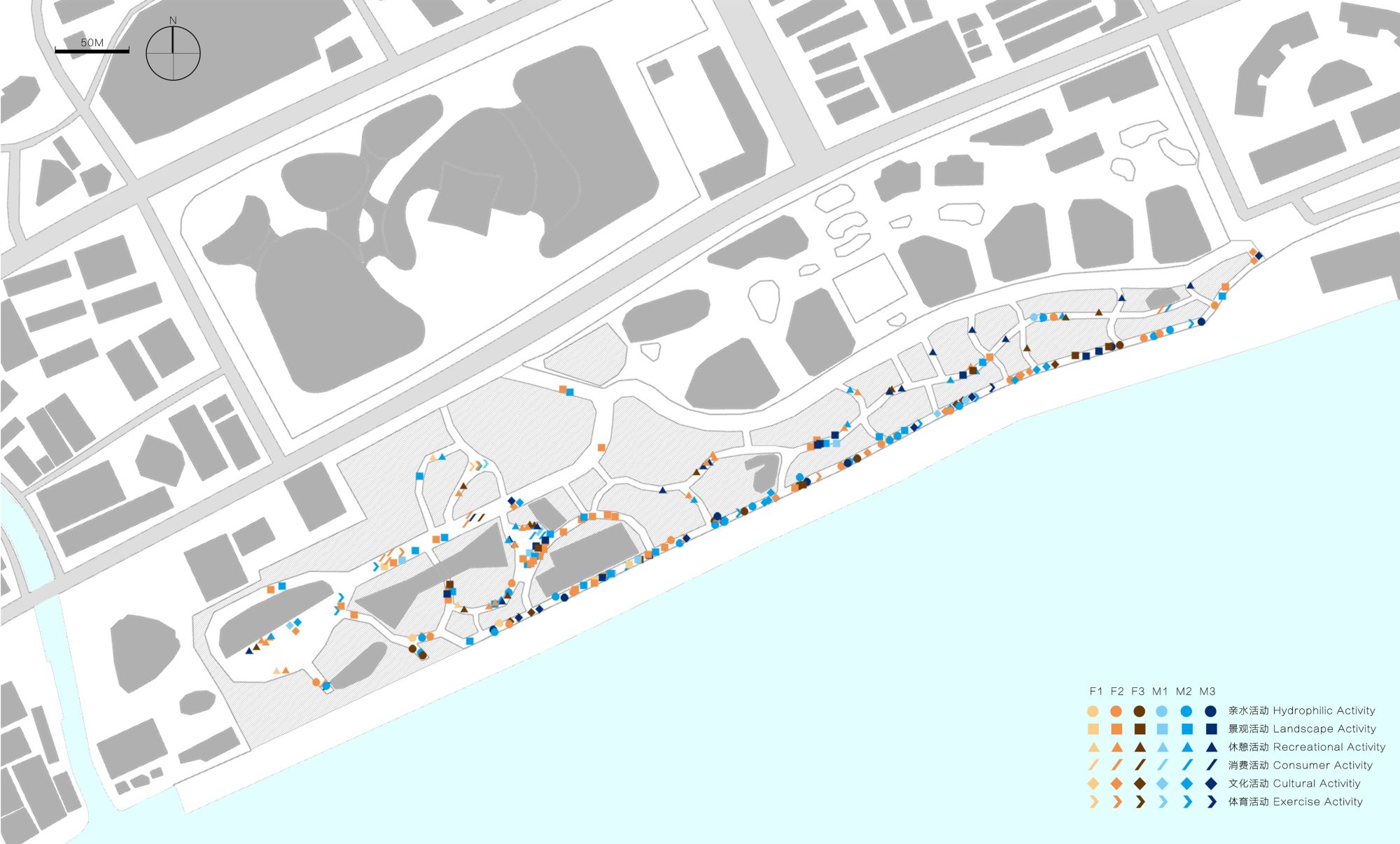
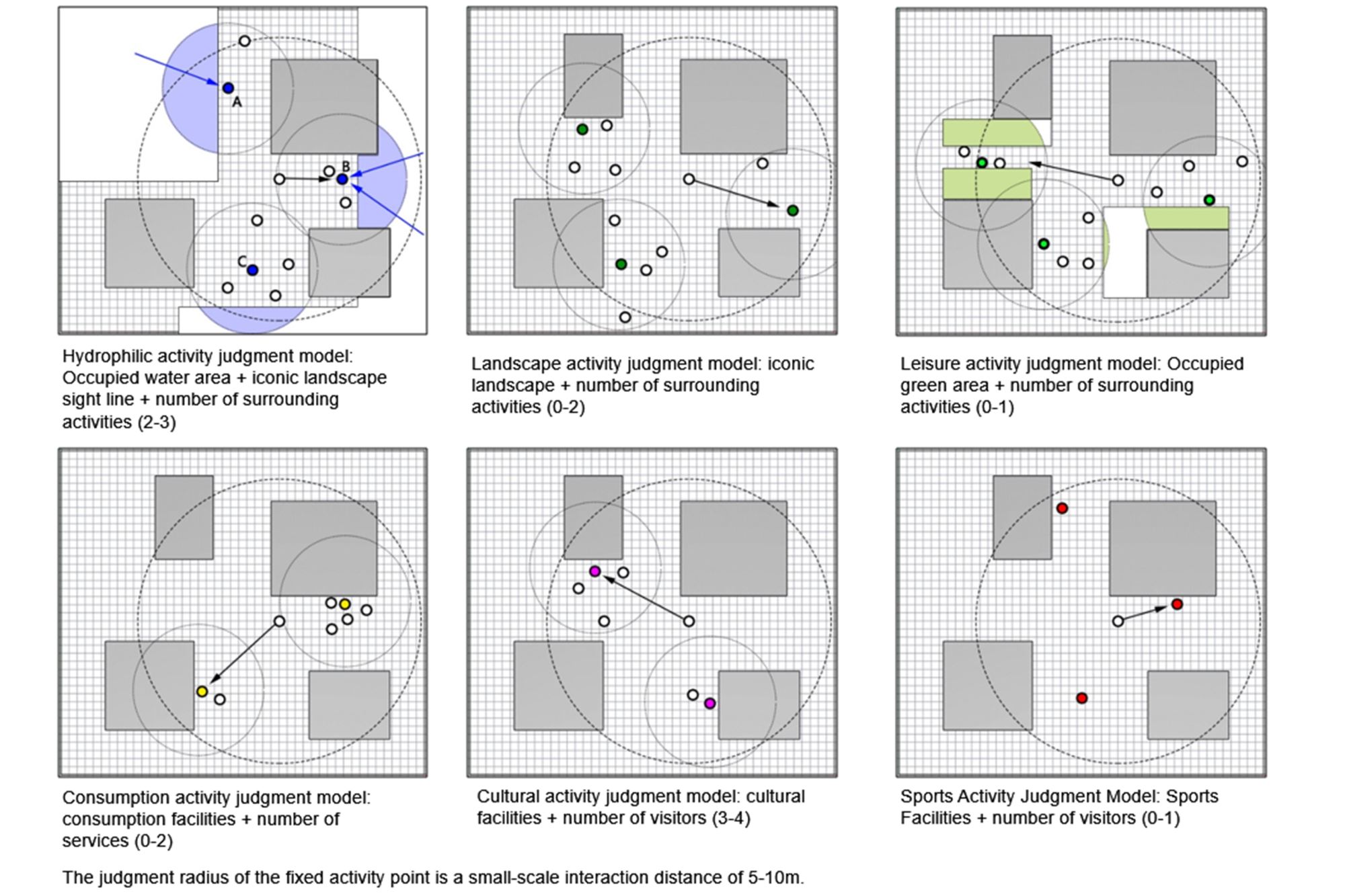
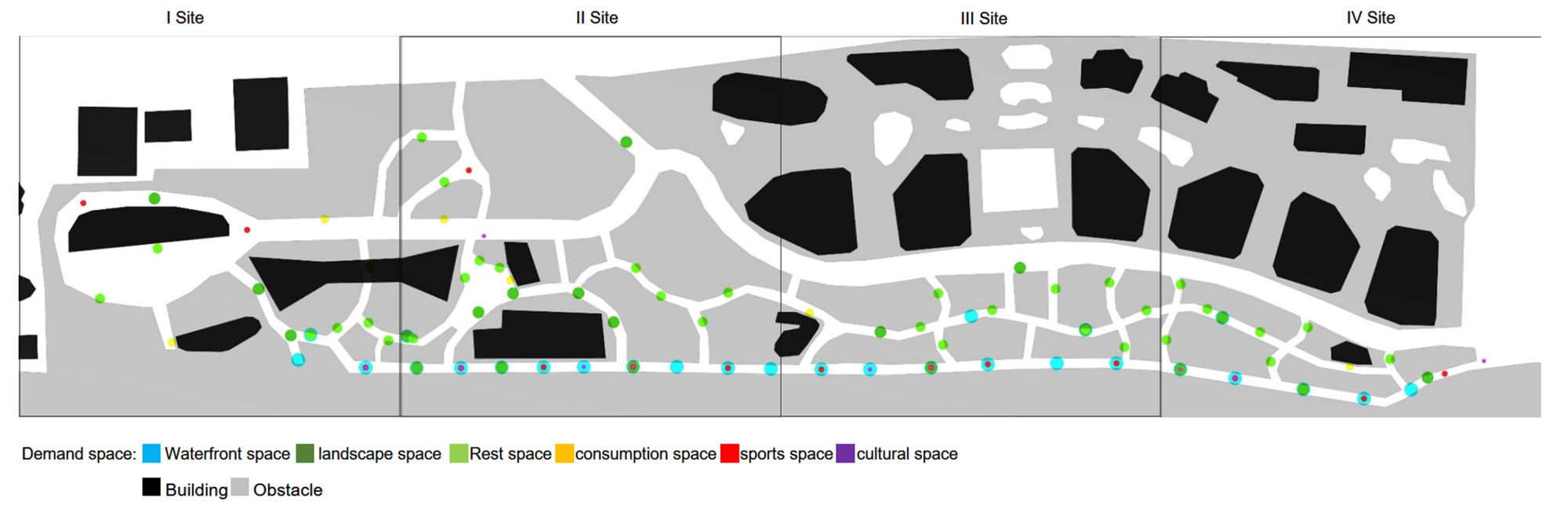
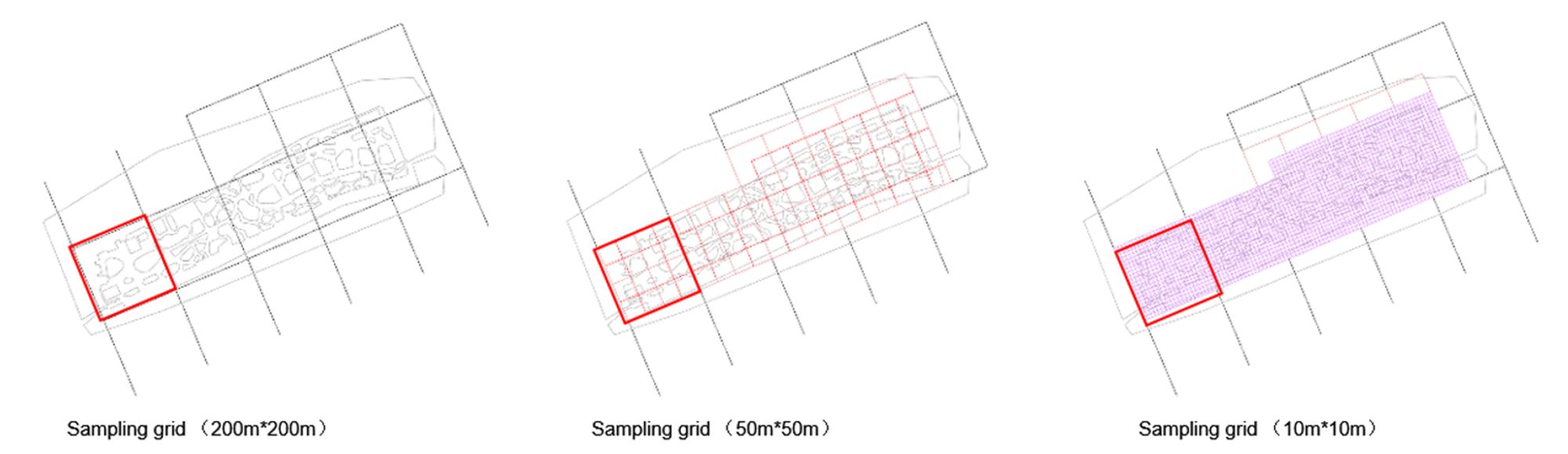
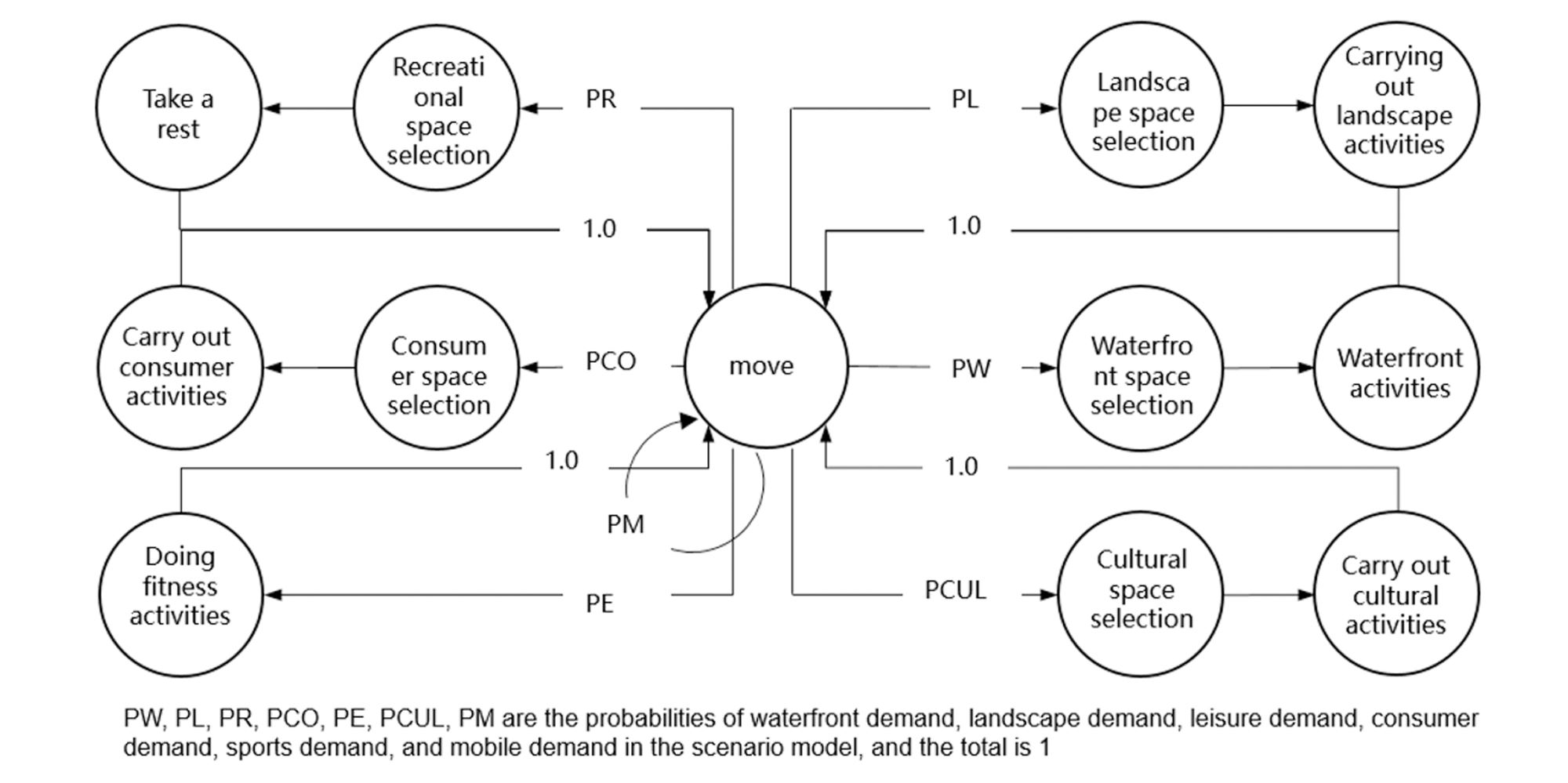
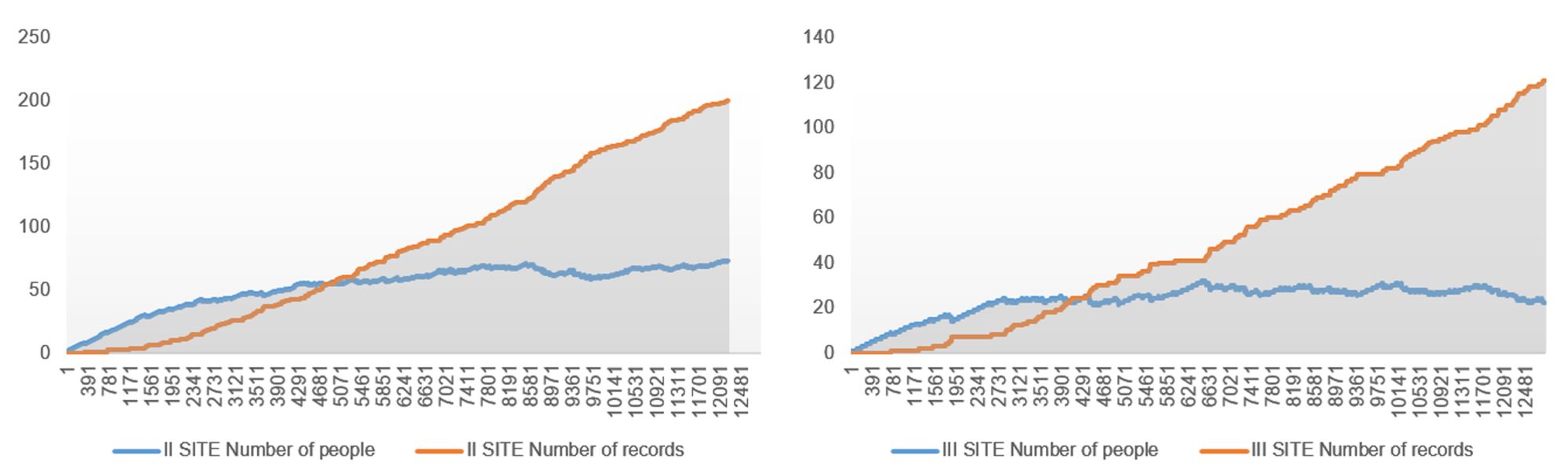
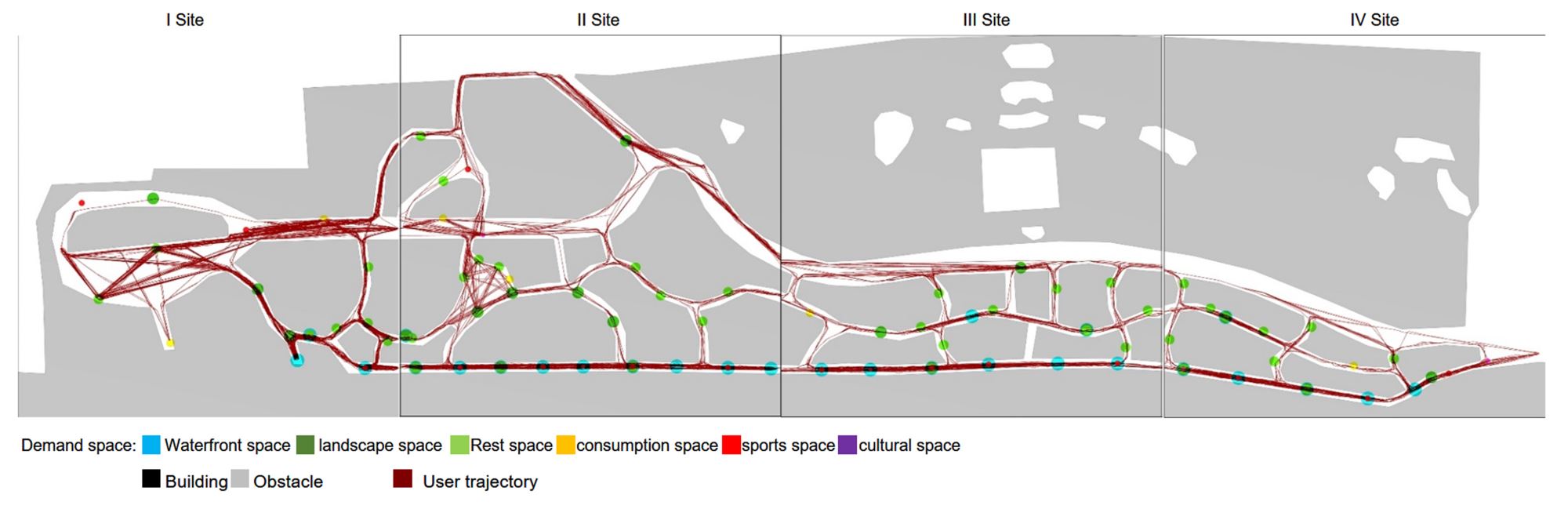
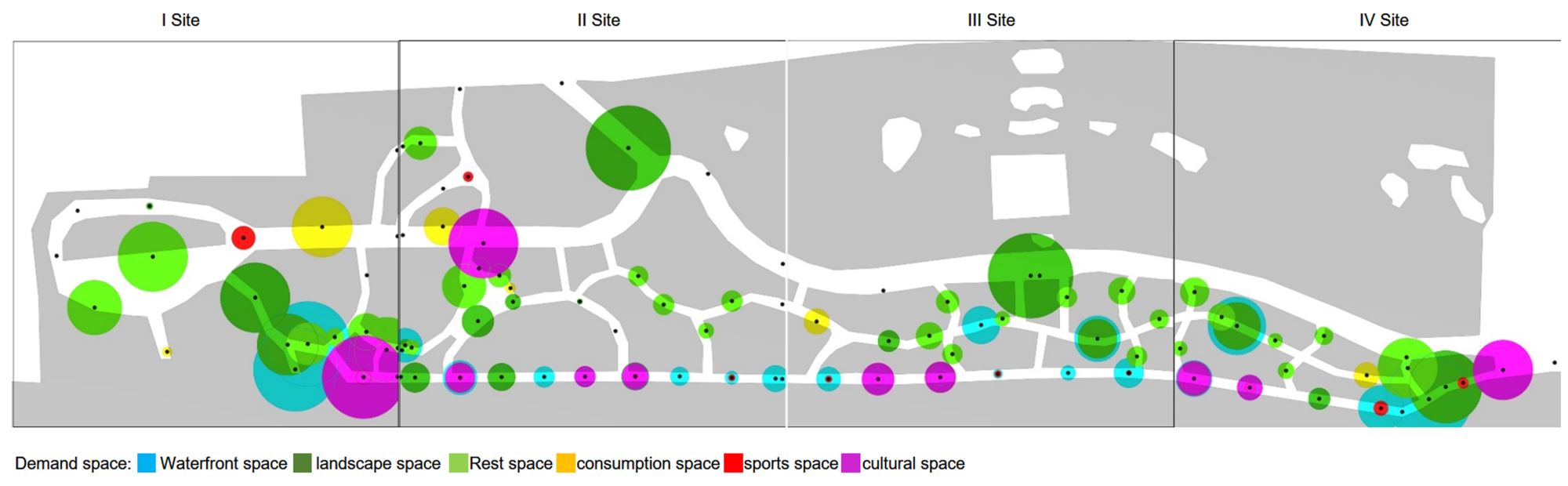
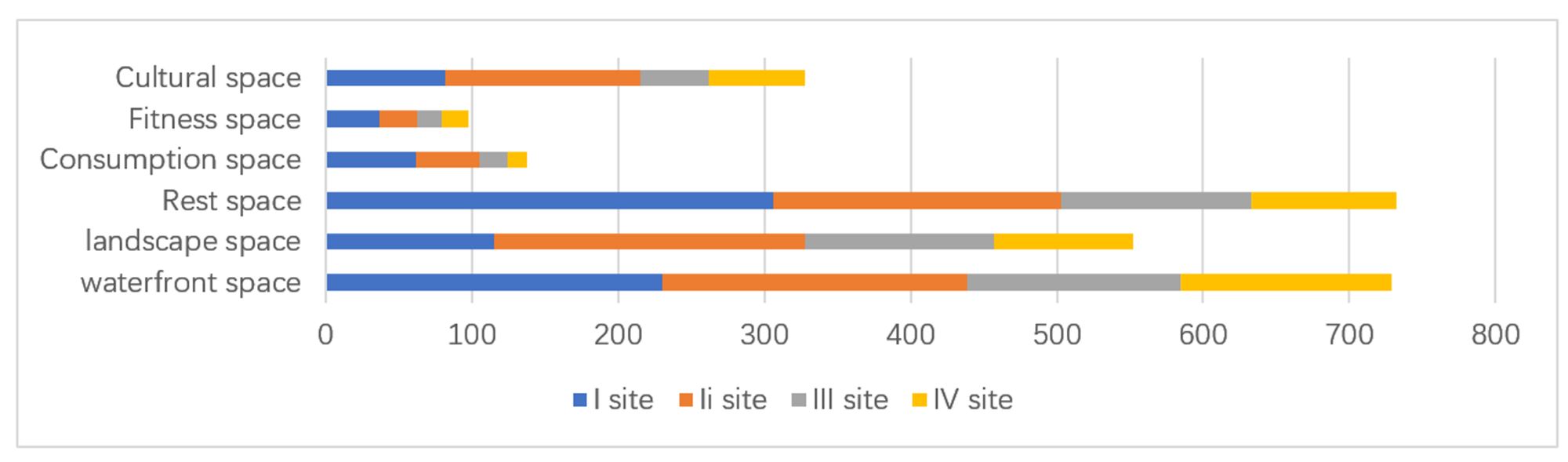
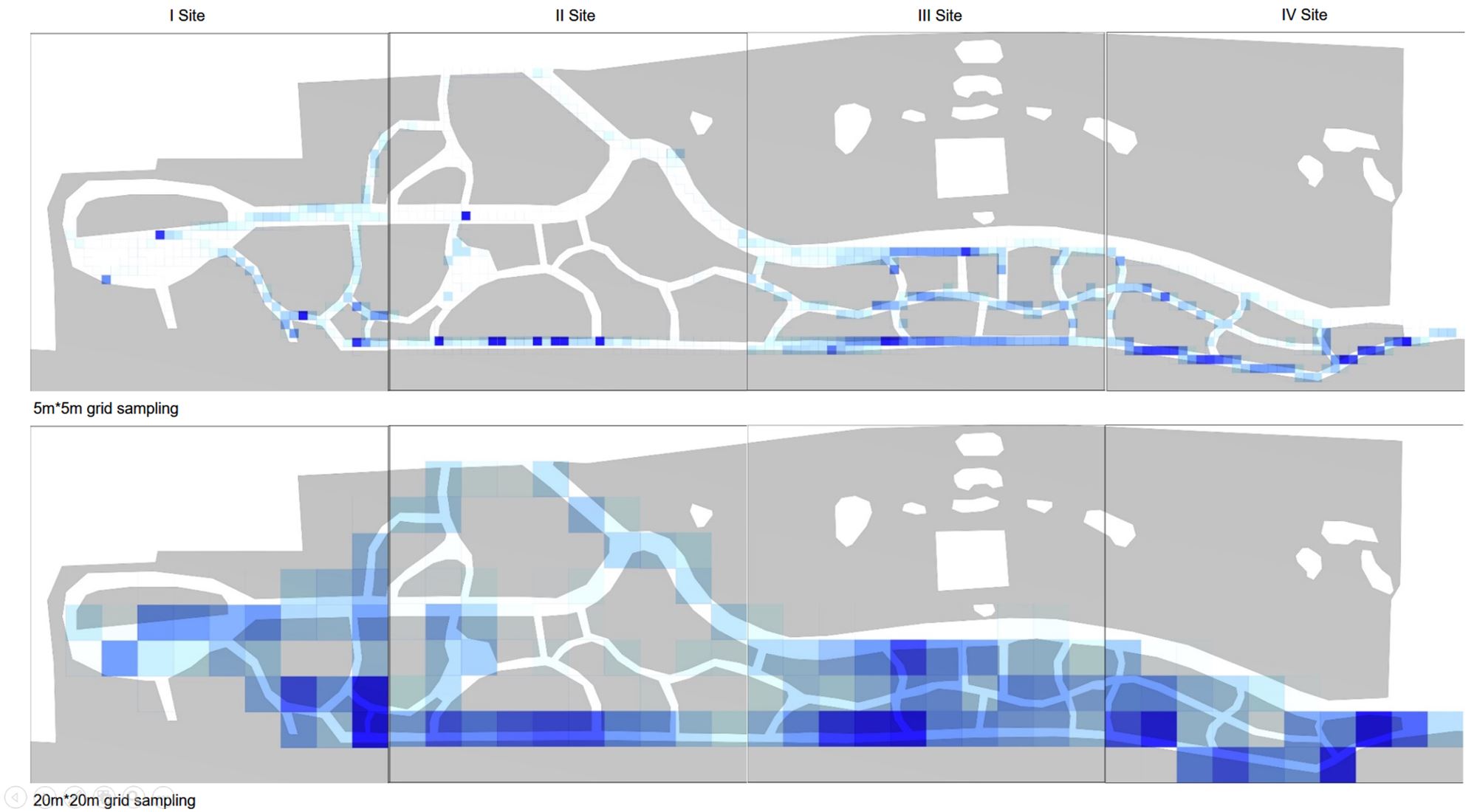
Abstract: This study uses a multi-agent behavioral simulation method to measure the use of public space on the North Bund waterfront. The multi-agent behavior model is mainly composed of a “scenario model” and a “micro-space selection model,” which are used to simulate the user’s behavior on how they use the space. The first step was to construct a multi-agent system behavior selection model (scenario behavior model and micro-space selection model) based on three data types consolidated from the North Bund public space: individual behavior, spatial behavior records, and spatial elements. Next, the behavior selection model and the spatial environment were combined to generate a simulation study. The third step derived information data, such as activity density and activity time distribution through spatial grid sampling. The simulation results indicate that the public space of the North Bund has an uneven distribution of activities, uneven distribution of activity time, and an uneven distribution of space utilization.





 loading......
loading......